The best 10 American most famous lawyer
Who are The best 10 American most famous lawyer?
Advertisement
Ruth Bader Ginsburg: As a U.S. Supreme Court Justice, Ruth Bader Ginsburg was a pioneering advocate for gender equality and women's rights. Before her judicial career, she co-founded the Women's Rights Project at the ACLU, where she successfully argued several landmark cases before the Supreme Court. Her tenacity and legal acumen made her a symbol of justice and progress.

 View All
View AllRuth Bader Ginsburg - Ruth Bader Ginsburg was known for her sharp intellect, fierce determination, distinctive collars, and dignified presence.

 View All
View AllThurgood Marshall - Thurgood Marshall was known for his sharp intellect, strong advocacy for civil rights, and historic Supreme Court legacy.

 View All
View AllClarence Thomas - Clarence Thomas is known for his deep voice, thoughtful demeanor, and strong presence as a Supreme Court Justice.

 View All
View AllSonia Sotomayor - Sonia Sotomayor is known for her intelligence, tenacity, compassion, and groundbreaking achievements as the first Latina Supreme Court Justice.

 View All
View AllAntonin Scalia - Antonin Scalia was known for his sharp intellect, charismatic presence, incisive wit, and unwavering commitment to originalism.

 View All
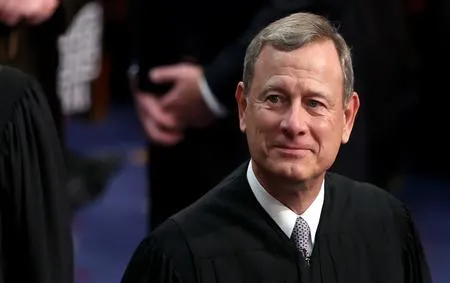
View AllJohn Roberts - John Roberts possesses sharp intelligence, a commanding presence, articulate speech, and a balanced, judicious demeanor.

 View All
View AllElena Kagan - Elena Kagan is known for her intelligence, strong presence, articulate communication, and a keen sense of justice.

 View All
View AllWilliam Rehnquist - William Rehnquist was known for his sharp intellect, distinctive judicial philosophy, and strong conservative principles.

 View All
View AllRobert H. Jackson - Robert H. Jackson was known for his eloquence, integrity, sharp legal mind, and commitment to justice.

 View All
View AllLouis Brandeis - Louis Brandeis was known for his intelligence, advocacy for social justice, progressive ideals, and eloquent legal reasoning.
The best 10 American most famous lawyer
1.
Ruth Bader Ginsburg
Ruth Bader Ginsburg (1933-2020) was an influential American jurist and Supreme Court Justice known for her steadfast advocacy for gender equality and civil rights. Appointed to the Supreme Court in 1993 by President Bill Clinton, she became the second woman to serve on the nation’s highest court. Ginsburg was a trailblazer in her legal career, co-founding the Women’s Rights Project at the American Civil Liberties Union and arguing several landmark cases before the Supreme Court. Her powerful dissents and commitment to justice earned her a reputation as a cultural icon and a symbol of resilience in the fight for equality.
Pros
Inspiration for gender equality
legal legacy of justice
advocacy for civil rights
role model for resilience
promotion of diversity
encouragement of civic engagement
profound cultural impact.
Cons
Limited personal connection due to her status
potential for polarizing opinions
high expectations leading to disappointment
overshadowed by her legacy
intense public scrutiny.
2.
Thurgood Marshall
Thurgood Marshall (1908-1993) was a pioneering American civil rights lawyer and the first African American Supreme Court Justice. Born in Baltimore, Maryland, he graduated from Lincoln University and earned his law degree from Howard University. Marshall gained national prominence as the chief counsel for the NAACP, where he successfully argued landmark cases, including Brown v. Board of Education, which helped dismantle racial segregation in public schools. Appointed to the Supreme Court in 1967 by President Lyndon B. Johnson, Marshall championed civil rights, social justice, and the protection of individual liberties throughout his 24-year tenure, leaving a lasting legacy in American law.
Pros
Inspiration from his legacy
understanding civil rights history
empowerment through justice advocacy
awareness of legal reforms
motivation for social change
appreciation for diversity in law.
Cons
Limited public recognition compared to other figures
potential misinterpretations of his legacy
overshadowed by contemporary issues
risk of politicization of his achievements
historical context may be overlooked.
3.
Clarence Thomas
Clarence Thomas is an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, having been appointed by President George H.W. Bush in 1991. Born on June 23, 1948, in Pin Point, Georgia, he grew up in a poor family and faced significant challenges in his early life. Thomas attended the College of the Holy Cross and later earned his law degree from Yale Law School. Known for his conservative judicial philosophy, he often emphasizes originalism and textualism in his interpretations of the Constitution. Thomas is also the Court's longest-serving member, known for his often-quiet presence during oral arguments.
Pros
Influential judicial philosophy
unique perspective on constitutional interpretation
commitment to originalism
advocacy for individual rights
promotion of civil discourse
encouragement of diverse viewpoints
respect for legal traditions.
Cons
Controversial judicial decisions
perceived lack of transparency
limited public engagement
potential influence of personal beliefs
underrepresentation of diverse perspectives
polarizing figure in American politics.
4.
Sonia Sotomayor
Sonia Sotomayor is an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, nominated by President Barack Obama in 2009. Born on June 25, 1954, in The Bronx, New York, she is the first Latina and Hispanic member of the Court. Sotomayor's early life was shaped by her Puerto Rican heritage and the challenges of growing up in a low-income neighborhood. She graduated from Princeton University and earned her law degree from Yale Law School. Known for her keen insights and advocacy for social justice, Sotomayor has become a prominent voice on issues such as race, gender, and civil rights.
Pros
Inspiration for diversity
advocacy for justice
representation of marginalized voices
insight into the judicial process
empowerment through personal narrative
encouragement of resilience and perseverance.
Cons
Political polarization
controversial rulings
perceived liberal bias
potential for judicial activism
criticism from conservative groups
personal life scrutiny
healthcare and immigration stances debated.
5.
Antonin Scalia
Antonin Scalia (1936-2016) was an influential Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, serving from 1986 until his death. Appointed by President Ronald Reagan, Scalia was known for his robust defense of originalism and textualism in constitutional interpretation, advocating for a strict adherence to the Constitution's text and the framers' intent. His sharp intellect, fiery rhetoric, and often-confrontational style made him a prominent figure in American jurisprudence. Scalia's opinions and dissents addressed a wide range of issues, including free speech, gun rights, and religious liberty, leaving a lasting impact on the legal landscape of the nation.
Pros
Influential legal philosophy
originalist interpretation of the Constitution
clarity in judicial opinion
rigorous debate stimulation
advocacy for textualism
enhancement of legal discourse
historical significance in law.
Cons
Controversial opinions
polarizing judicial philosophy
perceived lack of empathy
rigid interpretation of the Constitution
undermining of civil rights
potential for judicial activism
divisive public persona.
6.
John Roberts
John Roberts is the Chief Justice of the United States, having been appointed to the Supreme Court in 2005 by President George W. Bush. Born on January 27, 1955, in Buffalo, New York, Roberts graduated from Harvard College and Harvard Law School. He previously served as a judge on the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit and worked in private practice and as a government attorney. Known for his conservative judicial philosophy, Roberts has played a pivotal role in key cases involving healthcare, voting rights, and corporate regulation, often seeking to maintain the Court's institutional integrity amidst political pressures.
Pros
Enhanced leadership skills
improved team collaboration
strategic thinking development
increased creativity
expanded networking opportunities
personal growth
effective communication strategies
greater adaptability to change.
Cons
Controversial rulings
perceived partisanship
inconsistent judicial philosophy
limited transparency
potential bias
lack of accountability
influence on public policy
polarizing figure
legal unpredictability.
7.
Elena Kagan
Elena Kagan is an Associate Justice of the United States Supreme Court, having been nominated by President Barack Obama and confirmed in 2010. Born on April 28, 1960, in New York City, she is the fourth woman to serve on the Court. Kagan attended Princeton University, the University of Oxford as a Marshall Scholar, and Harvard Law School, where she was the first female dean. Before her appointment to the Supreme Court, she served as Solicitor General of the United States and held various positions in academia and government. Kagan is known for her pragmatic approach to law and her expertise in constitutional issues.
Pros
Insightful legal analysis
strong advocacy for justice
commitment to equality
diverse perspectives
influential judicial opinions
dedication to public service
role model for aspiring lawyers.
Cons
Limited judicial experience prior to Supreme Court appointment
perceived liberal bias
potential lack of clarity in opinions
and controversial decisions on key issues.
8.
William Rehnquist
William Rehnquist was an influential American jurist who served as the 16th Chief Justice of the United States from 1986 until his death in 2005. Appointed by President Richard Nixon in 1972 as an Associate Justice, Rehnquist was known for his conservative judicial philosophy and a strong emphasis on states' rights. His tenure as Chief Justice was marked by significant decisions that shaped constitutional law, particularly in areas like federalism, criminal procedure, and civil rights. Rehnquist's leadership helped steer the Court towards a more conservative direction, leaving a lasting impact on the American legal landscape.
Pros
Influential judicial philosophy
strong leadership
commitment to conservative values
significant Supreme Court decisions
judicial independence
clarity in legal reasoning
historical impact on American law.
Cons
Controversial judicial decisions
perceived bias towards conservative ideologies
limited civil rights advancements
criticism for handling of Native American cases
lack of empathy in rulings.
9.
Robert H. Jackson
Robert H. Jackson (1892-1954) was an influential American jurist and lawyer, renowned for his role as an Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court from 1941 until his death. A prominent figure in the legal field, Jackson served as the U.S. Attorney General and played a pivotal role in landmark cases, advocating for civil liberties and the separation of powers. He is perhaps best known for his work as the chief U.S. prosecutor at the Nuremberg Trials, where he sought justice for war crimes committed during World War II. Jackson's legacy endures through his impactful legal writings and commitment to human rights.
Pros
Insightful legal philosophy
profound historical impact
inspiration for justice
advocacy for human rights
exceptional judicial reasoning
commitment to international law
dedication to civil liberties.
Cons
Limited public recognition compared to contemporaries
complex legal language
potential bias in rulings
historical context may not resonate today
challenges in accessing comprehensive works.
10.
Louis Brandeis
Louis Brandeis (1856-1941) was an influential American lawyer, jurist, and advocate for social justice, best known as the first Jewish Supreme Court Justice. Appointed by President Woodrow Wilson in 1916, Brandeis championed progressive causes, including labor rights, women's suffrage, and the regulation of monopolies. His groundbreaking opinions emphasized the importance of individual liberties and the right to privacy, notably in the landmark case of Olmstead v. United States. A prominent figure in the legal community, Brandeis also played a vital role in the development of modern American jurisprudence, earning the title "the People's Attorney" for his commitment to public interest law.
Pros
Influential legal insights
advocacy for social justice
champion of privacy rights
progressive reforms
emphasis on transparency
inspiration for future generations
impactful judicial philosophy
rich historical legacy.
Cons
Controversial opinions
polarizing legal decisions
potential for judicial activism
complexities in interpreting his views
historical context may not align with modern values
limited accessibility of his writings.